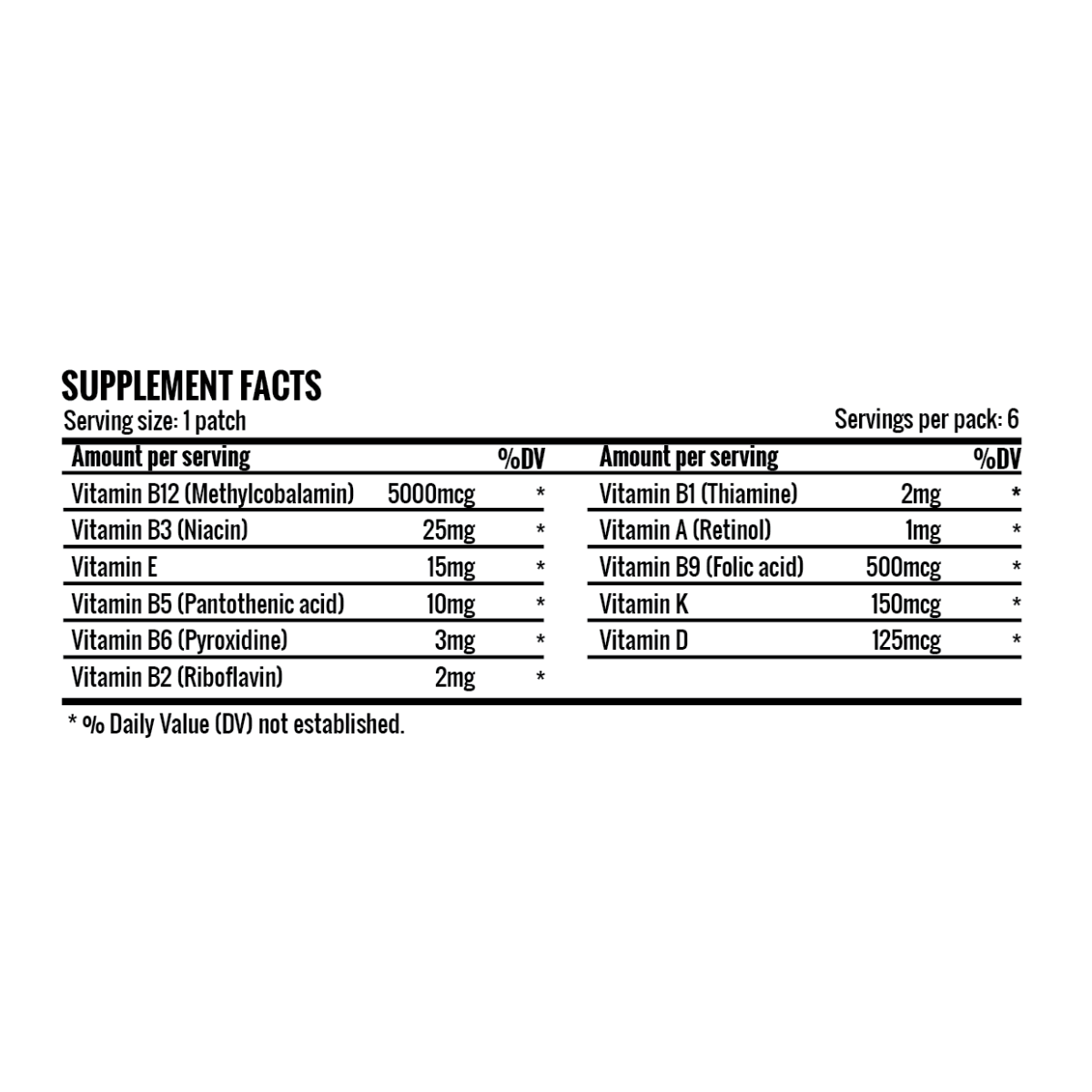
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in preserving health. Vitamin B12 deficiency can result in a variety of symptoms, such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and cognitive decline. Other vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms include anemia, constipation, appetite loss, weight loss, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause emotional and psychological symptoms such as depression, memory loss, and difficulty concentrating, in addition to physical symptoms. Low levels of vitamin B12 have been associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia, which makes these symptoms especially concerning for the elderly.
It is essential to remember that vitamin B12 deficiency is not always apparent, as symptoms may develop gradually over time. If you are concerned about your vitamin B12 intake or if you experience any of the above symptoms, it is recommended that you consult a healthcare professional. A sufficient intake of vitamin B12 can prevent deficiency and promote overall health.
History
In the middle of the 20th century, scientists were able to synthesize vitamin B12 and make it widely available as a dietary supplement.
How it works
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for numerous bodily processes. It is required for the creation of red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body. Vitamin B12 is also required for proper nervous system function and DNA synthesis, the body's genetic material. Vitamin B12 is also involved in the metabolism of folate, another essential B vitamin, and the conversion of food to energy.
Vitamin B12 is naturally present in a variety of foods derived from animals, including meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products. It is also available as a dietary supplement and in fortified foods, such as certain cereals and plant-based milk alternatives.
Vitamin B12 is absorbed by the body using a protein called intrinsic factor, which is produced by the stomach. The vitamin B12 is then transported to the liver, which stores it for future use.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can be caused by a variety of factors, including an inadequate diet, specific medical conditions, and certain medications. If you are concerned about your vitamin B12 intake or are at risk for deficiency, it is essential that you consult a healthcare professional. Vitamin B12 is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing deficiencies, which can result in a variety of symptoms.
Studies and Results
Numerous studies have examined the positive effects of vitamin B12 on brain and nervous system health. In one study, low vitamin B12 levels were associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia in the elderly. This suggests that adequate vitamin B12 intake may be necessary for maintaining cognitive function with age.
Another study found that vitamin B12 supplements improved depression symptoms and brain function in vitamin B12-deficient individuals. These findings indicate that vitamin B12 may be an effective treatment for individuals with low vitamin B12 levels and mood-related symptoms.
Multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease are among the neurological disorders that vitamin B12 may protect against, according to additional research. However, additional research is required to fully comprehend the function of vitamin B12 in these conditions.
In general, the studies on vitamin B12 and brain and nervous system health indicate that an adequate intake of the vitamin is necessary for maintaining good overall health and preventing deficiencies that can result in a variety of symptoms. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine the correct dosage and formulation of vitamin B12 for your specific needs.
Recommended Dosage
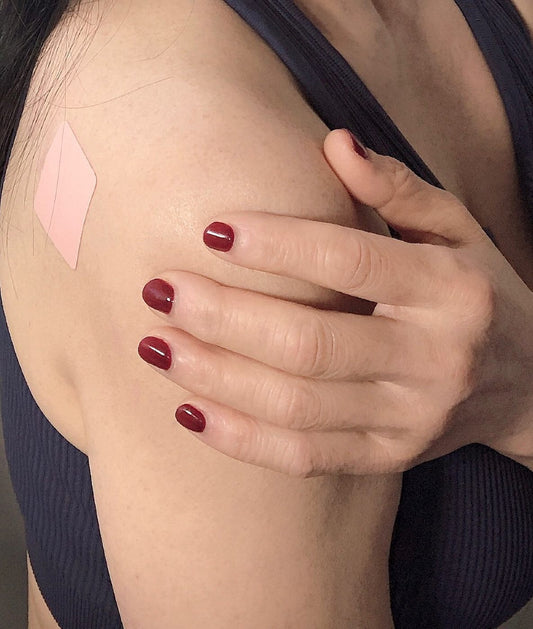
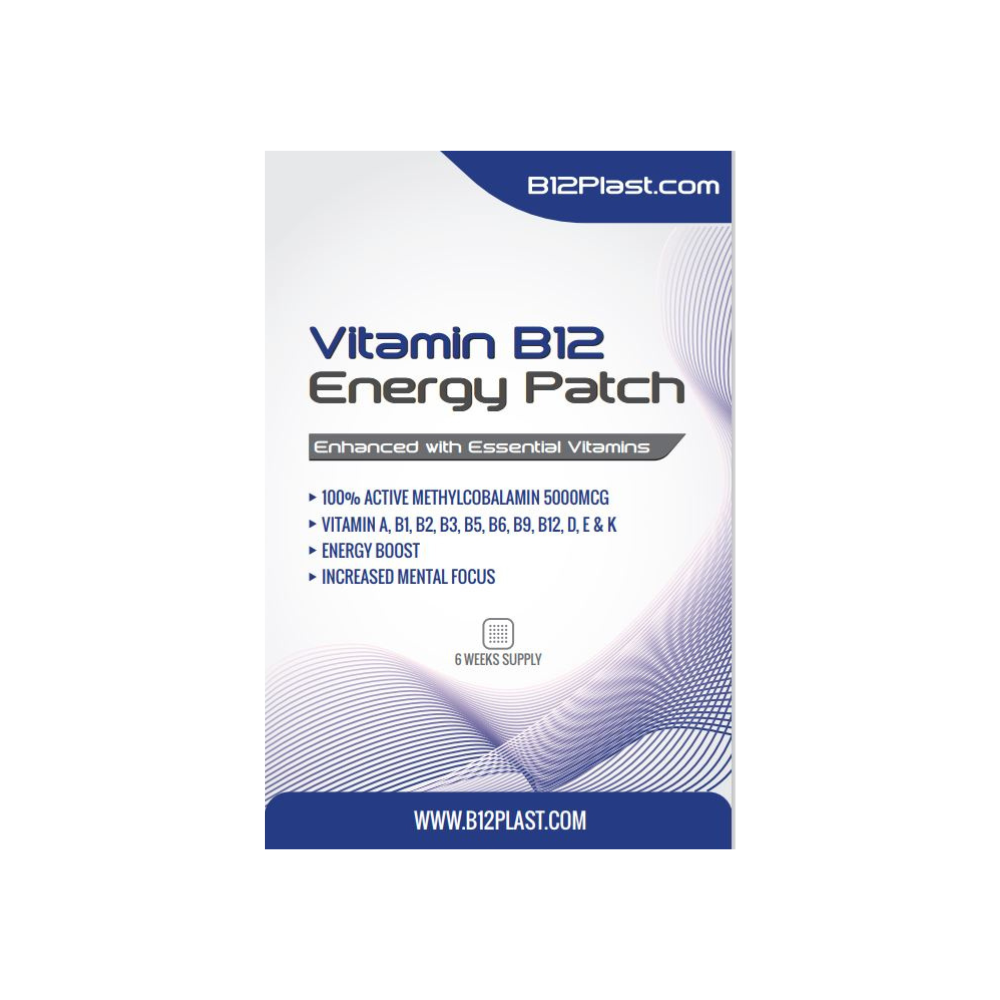
Vitamin B12 has a recommended daily allowance (RDA) of 2.4 micrograms per day for adults. However, certain individuals, such as those with a deficiency or poor absorption, may require higher doses. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional in order to determine the correct dosage for your individual needs. In addition, vitamin B12 patches that allow the body to absorb the nutrient through the skin are available for individuals who have difficulty swallowing pills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that is essential for proper brain and nervous system function. Vitamin B12 is essential for maintaining good health and preventing deficiencies, which can cause a variety of symptoms.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC329619/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3576830/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2845837/