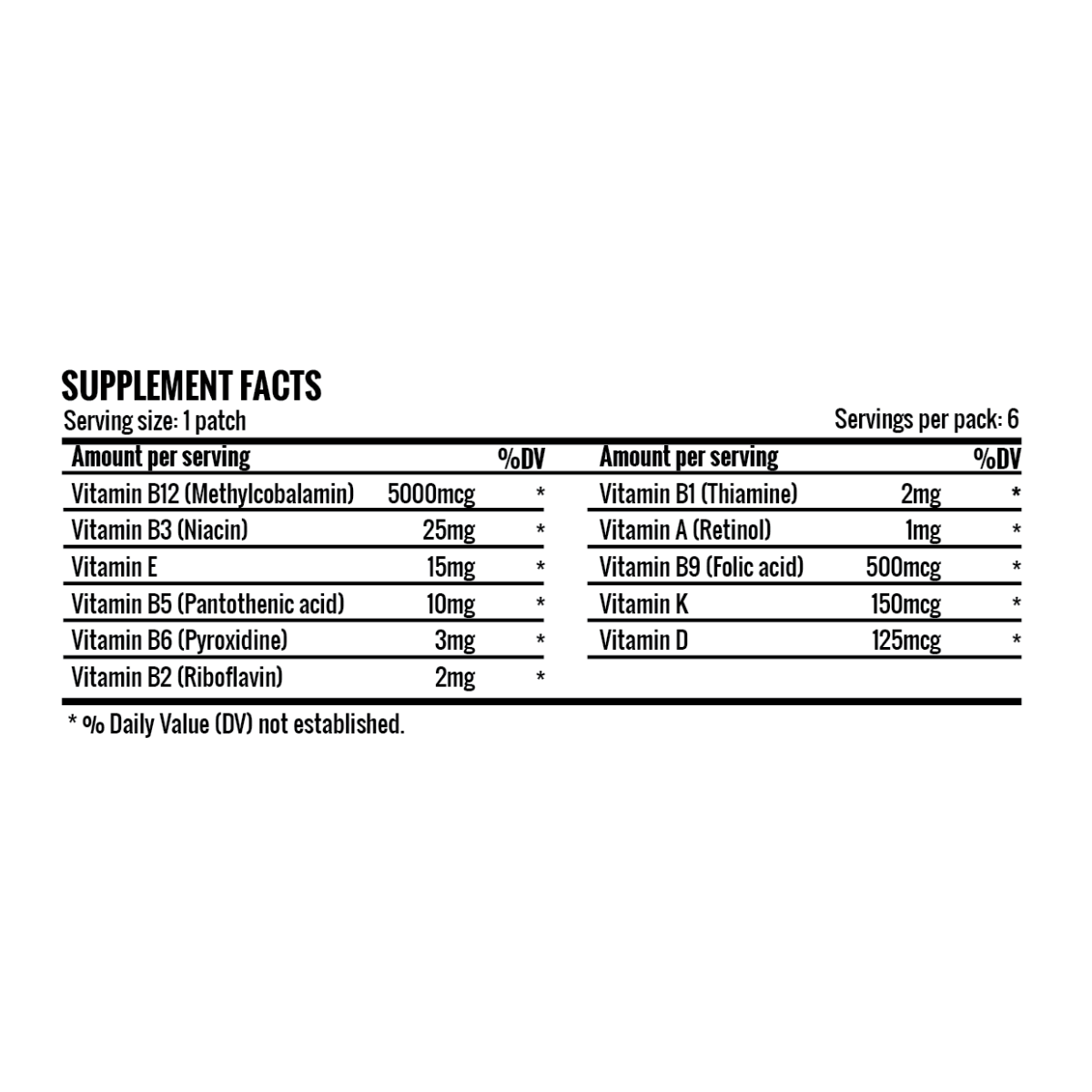
B12 Deficiency
Your body also needs B12 to make red blood cells and to keep your nerves healthy. It’s the only vitamin that contains a metal (cobalt) which gives it its name — cobalamin. You can’t get enough B12 from your diet without eating meat or dairy, which is why vegetarians and vegans are at risk of being deficient in this vitamin. The CDC reports that 8 percent of people 14 to 18 years old and 3 percent of adults over 50 have a low B12 level.
B12 is a big molecule, so it doesn’t get absorbed well in the gut even if you eat plenty of animal products. Most people store several years worth of B12 in their liver, but if you don’t eat meat for a long time, then you won’t have much stored away for later.
Who's At Risk Of B12 Deficiency?
Luckily, it’s easy to determine if you have a B12 deficiency. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), “Blood tests can tell whether your body has enough stores of vitamin B12 to last months, or whether you are running low and need more right away.”
Your doctor can test your blood for vitamin B12 levels. If you find that you are deficient in B-Vitamin 12, the NIH recommends that you take a daily supplement containing B12. However, it is recommended that you consult with your doctor before beginning any new nutritional regimen.
Signs Of B12 Deficiency
-
Fatigue
-
Weakness
-
Dizziness
-
Headache
-
Confusion
-
Depression and irritability
-
Memory loss
-
Constipation, diarrhea, or gas
-
Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet (also known as paresthesia)
-
Loss of balance or unsteady gait (also known as ataxia)
A sore mouth or tongue is another sign of B12 deficiency. The red blood cells become abnormally large, which can cause some other symptoms, such as:
How to Increase Your B12 Levels Using Transdermal Patches
How to Increase Your B12 Levels Using Transdermal Patches
Many people choose to take a vitamin B12 supplement in the form of a sublingual tablet, but this method of ingestion can be inefficient. In general, under 5% of the B12 in a typical supplement pill is actually absorbed by the body.
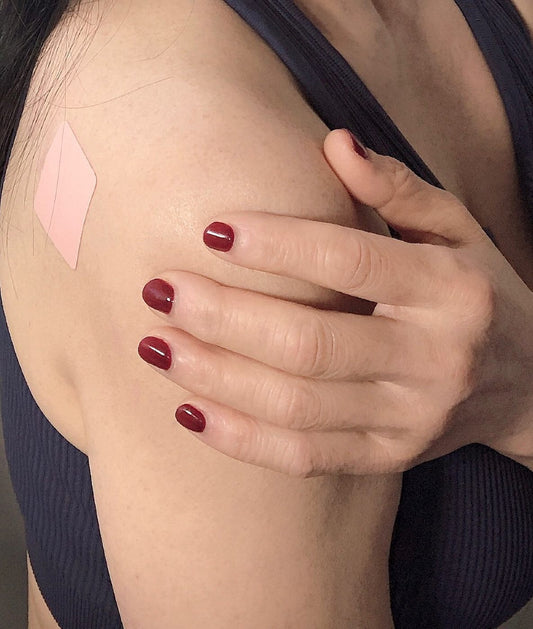
As an alternative, many people are turning to transdermal patches as a more effective way to increase their vitamin B12 levels. The patches are used on hairless skin areas (such as arms, legs or stomach) and contain microneedles that deliver the vitamin directly into your capillaries through your skin. This allows for about 80-90% absorption! Most people find this method not only easier but also much less intrusive than taking an oral supplement.
Understanding how this crucial vitamin can keep your body running at maximum capacity is key to managing your health.
So what is this vitamin and why do you need it? B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that plays an important role in your body. It does this by helping to make DNA, red blood cells and maintaining the health of your nerve cells. So ensuring you have enough B12 helps maximise the function of your entire body.
When vitamin B12 deficiency occurs, it can cause symptoms like fatigue, memory loss and soreness in your mouth - so feeling tired all the time could be down to low levels of B12! Other common symptoms include depression, pins & needles or tingling in the hands & feet, heart palpitations or lightheadedness when standing up quickly.
When looking at foods high in Vitamin B12 certain animal products are naturally very high in it such as beef liver, fish such as salmon and tuna or shellfish like clams and crabmeat. However many cereals are fortified with vitamin B12 so if you prefer to go vegan/vegetarian then consuming these cereals will help boost intake!
One way of increasing your intake is by using sublingual heath supplements (ones that go under the tongue), but for those who are not too keen on tablets or capsules - why not try a Vitamin Patch! These patches work by simply being stuck on any venous area such as lower back, ankle or wrist for 24 hours - allowing for quick absorption into the body through skin patches - ideal for those who want a fuss free method of consumption!