Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that is essential for many bodily functions, including red blood cell production. Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body, and a Vitamin B12 deficiency can result in anemia, a condition in which the body lacks sufficient red blood cells. Anemia can result in numerous symptoms, including:
- Anemia can result in feelings of fatigue and weakness because there are insufficient red blood cells to transport oxygen to the body's cells and tissues.
- As the body is not receiving enough oxygen, anemia can cause shortness of breath, especially during physical activity.
- Anemia can result in pale skin, as there are insufficient red blood cells to give the skin its normal, healthy color.
- Anemia can cause dizziness or lightheadedness because the brain is not receiving sufficient oxygen.
- As the heart must work harder to compensate for the lack of oxygen in the body, anemia can cause an irregular heartbeat or heart palpitations.
- Anemia can cause the hands and feet to feel cold because there is insufficient oxygen being circulated to these areas of the body.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, you should consult a medical professional to determine the cause. Vitamin B12 deficiency may be the cause, and supplementation with the nutrient may be required to alleviate these symptoms.
History
1948 marks the beginning of Vitamin B12's recorded history, when it was first isolated. Since then, it has been the subject of extensive research into its various health benefits. Vitamin B12 is naturally present in animal products such as meat, fish, and dairy, and it is also available in supplement form.
How it works
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that is crucial for many bodily processes. It aids in the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. Without sufficient red blood cells, the body can become anemic, resulting in symptoms such as fatigue and shortness of breath.
Vitamin B12 aids in maintaining the health of the skin, hair, and nails, in addition to its role in red blood cell production. It participates in the synthesis of DNA and the transformation of food into energy. Vitamin B12 is also necessary for healthy brain and nervous system function.
Vitamin B12 is naturally present in foods derived from animals, such as meat, fish, and dairy. It is also available in supplement form. Vitamin B12 is absorbed by the body in the small intestine with the aid of intrinsic factor.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is relatively common and can be caused by a lack of dietary intake, problems with absorption, or the use of certain medications. If you suspect you have a Vitamin B12 deficiency, you should consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and discuss treatment options. Vitamin B12 supplementation may be required to correct a deficiency and alleviate associated symptoms.
Studies and Results
Numerous studies have demonstrated that vitamin B12 deficiency-related conditions can be effectively treated with the nutrient supplement.
According to one study, daily supplementation with Vitamin B12 increased red blood cell production and decreased anemia symptoms. Vitamin B12 supplementation improved cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment, according to another study.
Vitamin B12 has also been associated with potential mood and mental health benefits. According to a number of studies, Vitamin B12 supplementation can enhance mood and diminish feelings of stress and anxiety. Vitamin B12 may reduce the risk of developing certain autoimmune diseases and improve asthma symptoms, according to additional research.
Although the results of these studies are encouraging, it is important to note that additional research is necessary to fully comprehend the potential benefits of Vitamin B12 and to determine the optimal dosage and duration of supplementation. Always consult a healthcare professional prior to beginning a new supplement regimen.
Recommended Dosage
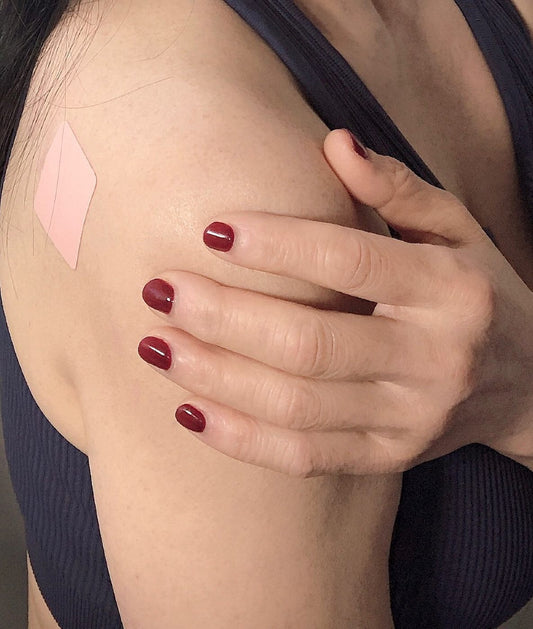
For adults, 2.4 micrograms of vitamin B12 per day is advised. However, those at risk of deficiency, like vegetarians and vegans, expectant and nursing mothers, and the elderly, might need higher doses. Tablets, capsules, and even a b12 transdermal patch that is applied to the skin for immediate absorption are all available forms of vitamin B12. It is crucial to keep in mind that the form of a vitamin B12 supplement may have an impact on its bioavailability and absorption; for instance, sublingual or chewable forms may have a higher bioavailability than tablets or capsules. It is advised to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the best form and dosage for your particular requirements.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that is essential for the production of red blood cells and the proper functioning of the body. Vitamin B12 supplementation is an effective method for treating anemia and other conditions caused by a deficiency in the nutrient. Before beginning a new supplement regimen, make sure to always adhere to the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional.
References
-
"Vitamin B12: Fact Sheet for Health Professionals." (n.d.). National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. Retrieved from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/
-
"Vitamin B12 Deficiency." (2019, August 26). Mayo Clinic. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vitamin-b12-deficiency/symptoms-causes/syc-20355089