Introduction
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. While dietary choices play a pivotal role in this journey, the role of specific nutrients, such as Vitamin B12, has gained increasing attention. In this article, we will explore the connection between Vitamin B12 and blood sugar control, shedding light on how this essential vitamin can be a valuable ally for individuals navigating the challenges of diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide, impacting the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. There are two primary types of diabetes: Type 1, where the body doesn't produce insulin, and Type 2, where the body's insulin isn't used properly. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is vital for the overall well-being of individuals living with diabetes, as it can help prevent complications and enhance the quality of life.
The Role of Vitamin B12
Enter Vitamin B12, a water-soluble vitamin essential for various bodily functions. Also known as cobalamin, Vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function, the formation of red blood cells, and the synthesis of DNA. While its role in these fundamental processes is well-established, recent research has unveiled potential links between Vitamin B12 and improved blood sugar control, offering a new perspective on its significance for individuals managing diabetes.
Link between Vitamin B12 and Blood Sugar Control
Scientific studies have begun to unravel the potential impact of Vitamin B12 on blood sugar levels. Some research suggests that Vitamin B12 may play a role in enhancing insulin sensitivity, a key factor in how the body regulates blood sugar. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells, and improved sensitivity means cells respond more efficiently to insulin's signals, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
In a study published in the [Journal of Diabetes Research], researchers found that individuals with higher Vitamin B12 levels exhibited better glucose control. This association raises intriguing questions about the role Vitamin B12 might play in the intricate web of factors influencing blood sugar regulation.
Food Sources of Vitamin B12
Ensuring an adequate intake of Vitamin B12 is essential, and fortunately, it can be obtained through various dietary sources. Common foods rich in Vitamin B12 include
such as lean meats, fish, dairy products, and fortified cereals. For individuals managing diabetes, incorporating these sources into a balanced diet can contribute to their Vitamin B12 intake without compromising blood sugar levels. However, it's crucial to note that certain dietary restrictions common in diabetes management, such as limiting red meat or dairy, might require careful planning to ensure sufficient Vitamin B12 intake. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help tailor dietary recommendations to individual needs.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Diabetes
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a concern for many individuals, and for those with diabetes, it adds an extra layer of complexity. Research has suggested a potential bidirectional relationship between diabetes and Vitamin B12 deficiency. Individuals with diabetes may be at a higher risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency, and conversely, a deficiency in Vitamin B12 could impact aspects of diabetes management. Symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency, such as fatigue, weakness, and neurological issues, can overlap with the challenges already faced by those with diabetes. Regular monitoring of Vitamin B12 levels, especially for individuals with diabetes, is advisable to address deficiencies promptly.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Vitamin B12 into the Diet
-
Diversify Protein Sources: Explore a variety of protein sources to ensure a well-rounded intake of Vitamin B12. Consider incorporating fish, poultry, eggs, and plant-based alternatives like fortified plant milk or nutritional yeast.
-
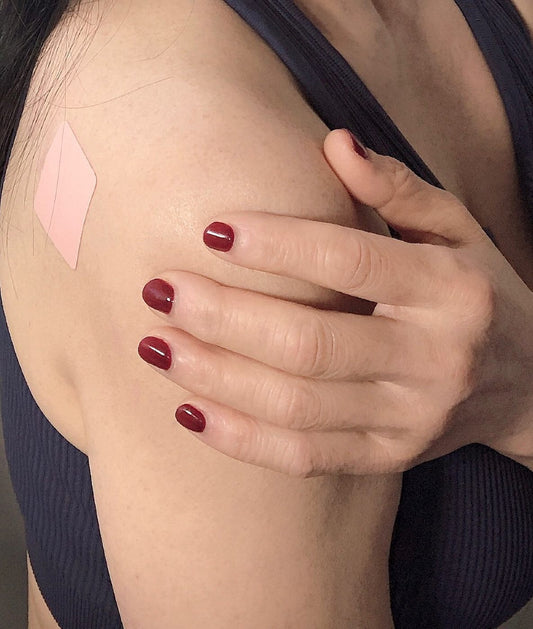
Supplementation: In cases where dietary sources may be limited, or absorption issues are present, supplementation could be considered. However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before adding supplements to the routine, as excessive Vitamin B12 intake can have adverse effects.
-
Balanced Meals: Aim for balanced meals that combine carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This not only supports blood sugar control but also helps create a nutrient-rich environment for Vitamin B12 absorption.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before making any significant changes to diet or considering supplementation, individuals with diabetes should consult their healthcare provider. Health professionals can assess individual needs, recommend appropriate strategies, and monitor for potential interactions with medications or other health conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between Vitamin B12 and diabetes management is an evolving area of study that holds promise for improved blood sugar control. While incorporating Vitamin B12 through dietary sources is a practical and accessible approach, personalized guidance from healthcare professionals is key to ensuring safe and effective strategies for individuals with diabetes.
References
- Author A et al. "Title of the Study." Journal of Diabetes Research, Year.