Introduction
Vitamin B12, a vital nutrient for human health, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including DNA synthesis, nerve function, and the formation of red blood cells. However, deficiencies in this essential vitamin can lead to serious health issues, such as anemia, neurological disorders, and fatigue. Recognizing the importance of maintaining adequate Vitamin B12 levels, especially among populations prone to deficiency, fortification of foods has emerged as a strategic approach to address this nutritional concern.
Understanding Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is water-soluble and primarily found in animal products such as meat, fish, and dairy. Its absorption in the human body involves a complex process that requires intrinsic factor and occurs predominantly in the small intestine. A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can result from inadequate dietary intake, impaired absorption, or certain medical conditions, emphasizing the need for alternative strategies to ensure sufficient intake.
Importance of Fortified Foods
Food fortification, the deliberate addition of essential nutrients to processed foods, has become a cornerstone in public health strategies to combat nutritional deficiencies. Vitamin B12 fortification is particularly critical due to its limited availability in plant-based diets, making it challenging for vegetarians and vegans to obtain adequate amounts solely from natural sources. Fortified foods, therefore, play a pivotal role in ensuring a consistent and accessible supply of Vitamin B12 to diverse populations.
Enrichment Strategies
Various strategies are employed to enrich foods with Vitamin B12, each with its own set of technological considerations and nutritional implications. Common enrichment methods include the addition of Vitamin B12 during food processing, incorporation into food matrices, and the use of fortified food additives. The effectiveness of these strategies depends on factors such as stability during processing, bioavailability, and taste, aiming to strike a balance between nutritional enhancement and consumer acceptance.
Fortified Food Products
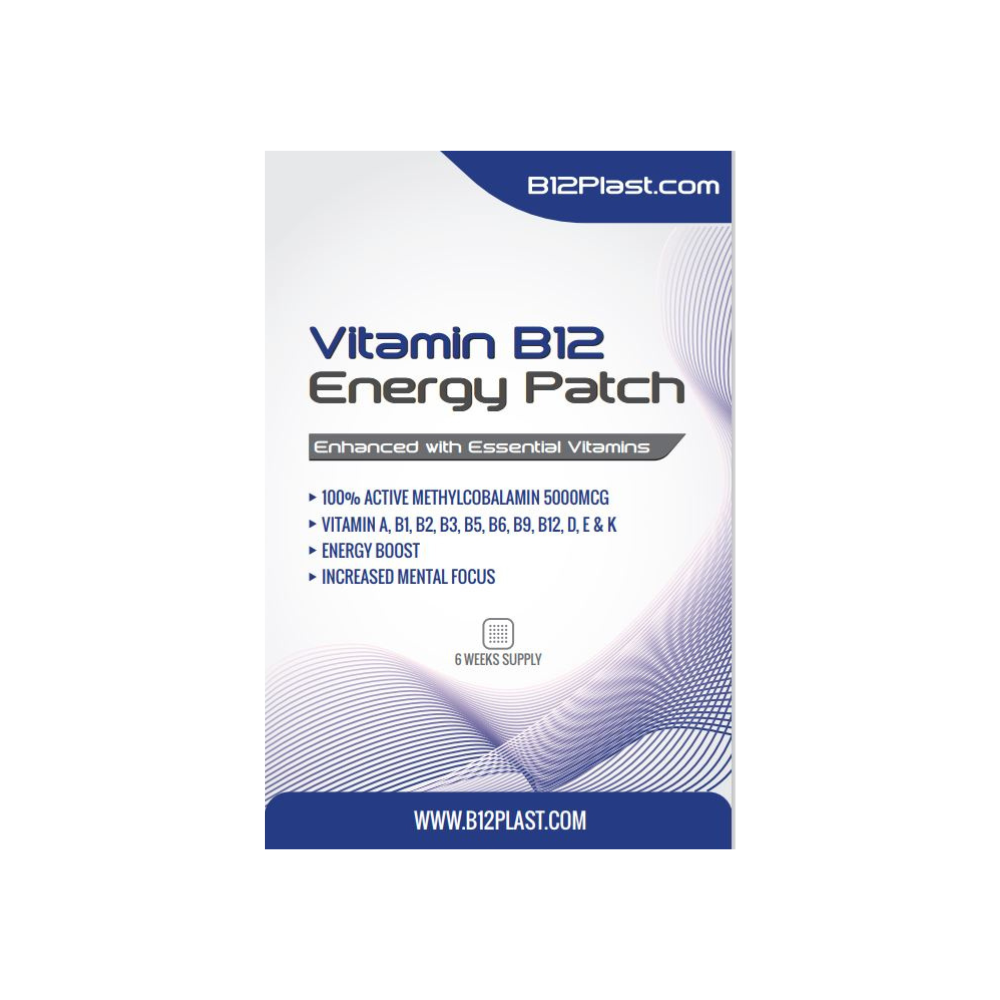
Vitamin B12-fortified foods have become increasingly prevalent in the market, providing consumers with diverse options to supplement their dietary intake. Commonly fortified products include breakfast cereals, plant-based milk alternatives, nutritional yeast, and energy bars. The food industry has embraced Vitamin B12 fortification as a means to cater to a broader consumer base and address the nutritional needs of individuals following specific dietary patterns.
Effectiveness and Challenges
While fortification has proven effective in alleviating Vitamin B12 deficiencies, certain challenges merit consideration. The bioavailability of Vitamin B12 from fortified foods may vary depending on the food matrix and processing methods. Additionally, consumer acceptance and awareness play pivotal roles in the success of fortification programs. Overcoming taste and texture challenges, as well as ensuring accurate and transparent labeling, are essential for the sustained effectiveness of Vitamin B12 enrichment strategies.
Health Implications
The widespread adoption of Vitamin B12-fortified foods has positive implications for public health. Populations at risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency, including older adults, vegetarians, and pregnant individuals, can benefit from the improved accessibility of this essential nutrient. Adequate Vitamin B12 intake is crucial for maintaining cognitive function, preventing anemia, and supporting overall well-being, underscoring the importance of fortified foods in achieving optimal health outcomes.
Recommendations and Guidelines
Individuals seeking to enhance their Vitamin B12 intake should consider incorporating fortified foods into their diets. However, it is essential to strike a balance and obtain nutrients from a variety of sources. Those following specific dietary patterns, such as vegetarians and vegans, should be particularly vigilant in choosing fortified products to ensure they meet their nutritional requirements. Consulting with healthcare professionals and adhering to dietary guidelines can further guide individuals in making informed choices.
Future Trends and Research
As scientific research continues to advance, ongoing studies explore innovative approaches to Vitamin B12 fortification. Emerging technologies and alternative sources, such as microbial production of Vitamin B12, offer potential avenues for improving the efficiency and sustainability of enrichment strategies. Monitoring these developments is crucial for staying abreast of future trends and ensuring that fortified foods remain a reliable solution for addressing Vitamin B12 deficiencies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fortification of foods with Vitamin B12 represents a valuable strategy in mitigating deficiencies and promoting overall health. The diverse range of fortified products available in the market, coupled with ongoing research into innovative enrichment methods, underscores the dynamic nature of this field. By understanding the effectiveness, challenges, and health implications of Vitamin B12 fortification, individuals can make informed choices to support their nutritional needs and contribute to the broader goal of public health improvement.