Infertility is a growing concern for many couples, and it can be a frustrating and emotionally draining experience for those attempting to start a family. About one-third of infertility cases are attributable to male partner issues. In addition to lifestyle factors like smoking, stress, and alcohol consumption, vitamin B12 deficiency can play a significant role in male infertility.
Vitamin B12 is essential for numerous aspects of health, including sperm production. This nutrient deficiency can cause a variety of fertility issues, including low sperm count and poor sperm motility. These symptoms can hinder a couple's ability to conceive and have a significant impact on their lives.
It is important to consider the role that vitamin B12 may be playing if you are struggling with infertility. Incorporating this nutrient into your diet or taking a supplement may be an effective method for increasing your fertility and chances of starting a family. Before beginning any new supplement regimen, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional, who can help determine the best form of B12 for your needs and recommend a safe and effective dosage.
History
Since its discovery in the 1940s, vitamin B12 has been extensively studied for its numerous health benefits. The correlation between B12 deficiency and male infertility was not established until the last several decades. Since then, numerous studies have been conducted to investigate this relationship and examine the role of B12 in male fertility.
How it works
Vitamin B12 is essential for sperm production for multiple reasons. First, it assists the body in producing DNA, the genetic material found in sperm. Sperm cells contain fifty percent of the genetic material required for fertilization; therefore, high-quality DNA is essential for fertility.
Second, B12 contributes to the maintenance of healthy sperm cells. Sperm cells are highly specialized and require specific nutrients for optimal function. Vitamin B12 protects the DNA in sperm cells from damage, thereby improving the overall quality of sperm and increasing the likelihood of fertilization.
Lastly, B12 aids in the production of red blood cells, which are responsible for transporting oxygen to all cells in the body, including sperm. Sperm cells need oxygen to produce energy and function normally; therefore, adequate oxygen levels are essential for fertility.
Vitamin B12 is indispensable for the production and maintenance of high-quality sperm. B12 deficiency in men can cause issues with sperm quality and fertility, making it more challenging for couples to conceive. Including this nutrient in the diet or taking a supplement can improve sperm quality and increase the likelihood of conception.
Studies and Results
Multiple studies have examined the connection between vitamin B12 and male fertility. A deficiency in this nutrient can have a significant impact on sperm quality and fertility, according to these studies.
In a study of 1,000 infertile men, those with low B12 levels had lower sperm counts and less motile sperm than those with normal B12 levels. Additionally, B12 supplementation improved sperm quality and increased the likelihood of conception.
The sperm count and motility of 40 men with fertility issues who took B12 supplements for three months increased significantly, according to a second study. These findings indicate that B12 supplementation may be an effective treatment for males with fertility issues.
Not all studies have found a positive correlation between B12 and fertility, it should be noted. Several studies have found that B12 supplementation has no significant effect on sperm quality. Given the overall body of evidence and the potential fertility benefits of B12, it is still worth considering as a potential solution.
The results of these studies indicate that a vitamin B12 deficiency may play a significant role in male infertility, and that supplementation with this nutrient may improve sperm quality and increase the likelihood of conception.
Recommended Dosage
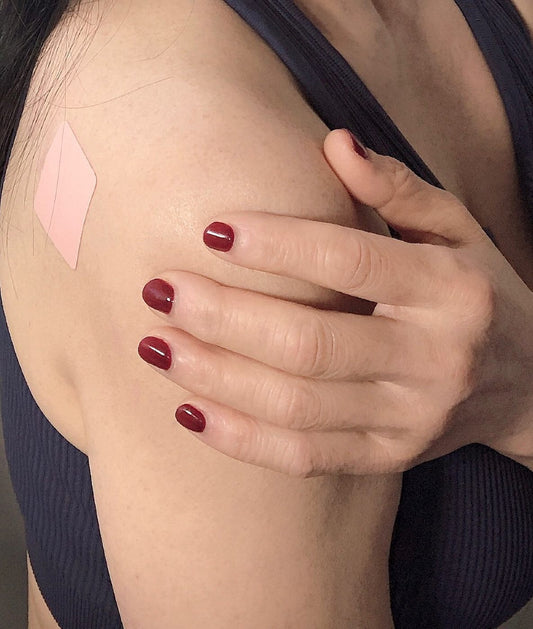
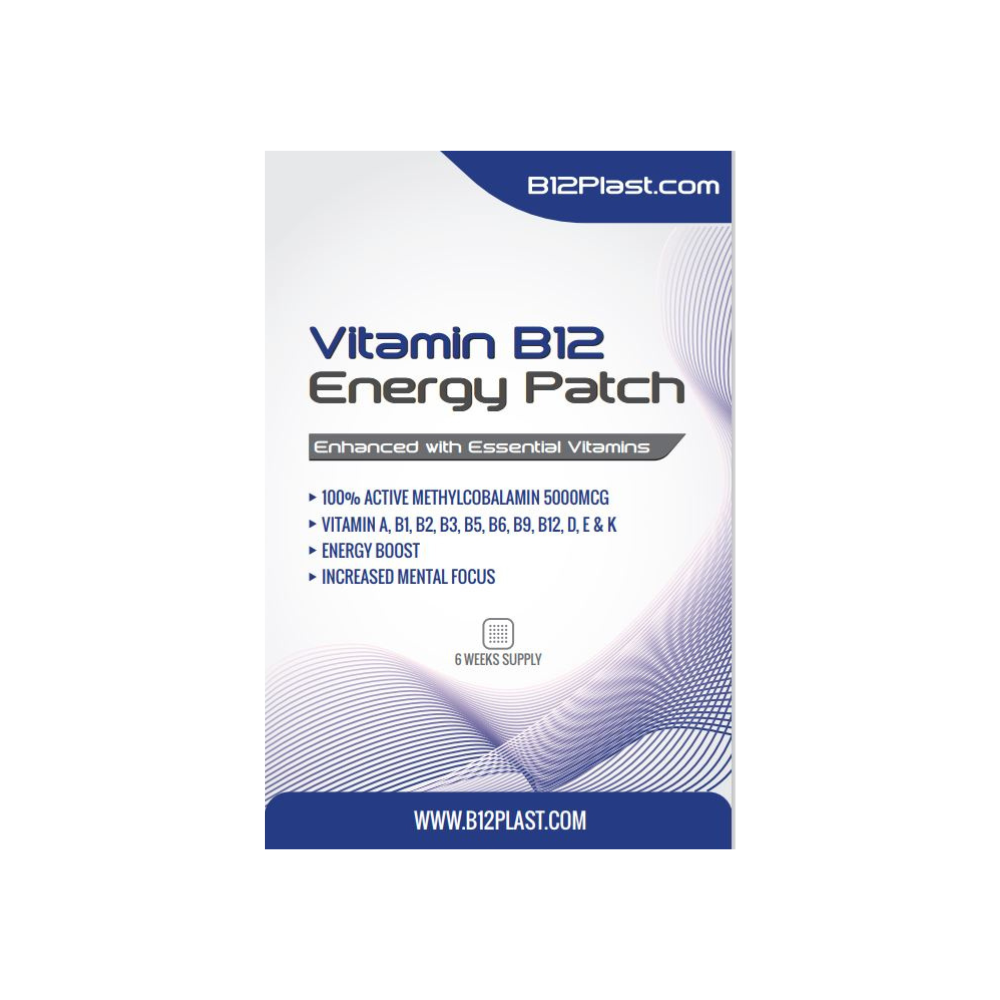
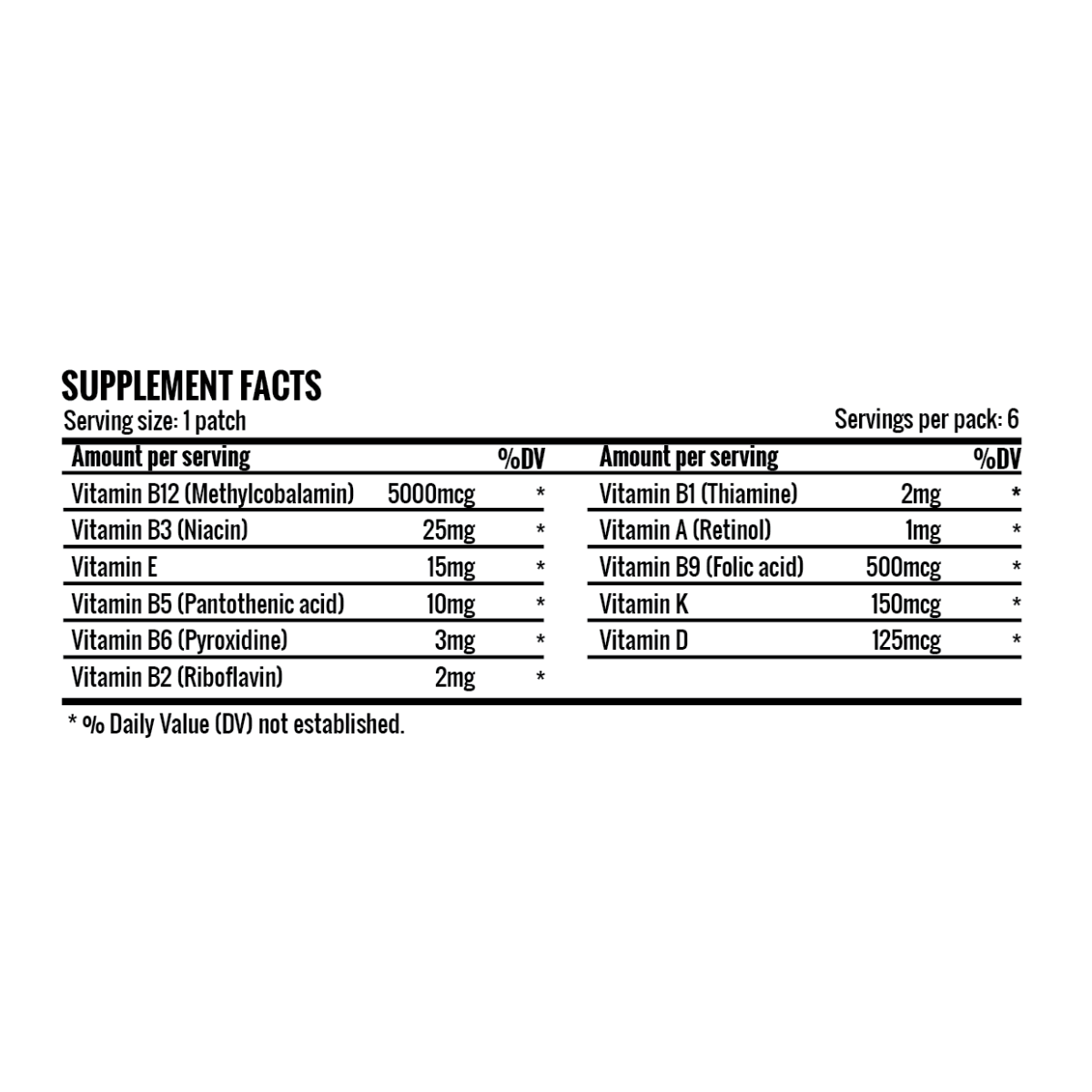
Men attempting to increase their fertility are advised to consume between 1,000 and 2,500 micrograms of vitamin B12 per day, according to the studies cited previously. There are various forms of vitamin B12, including oral supplements, injections, and transdermal patches. Those who have difficulty absorbing B12 orally may benefit most from a b12 transdermal patch, which delivers the nutrient directly into the bloodstream through the skin.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in male fertility. If you are struggling with infertility, incorporating vitamin B12 into your diet or taking a supplement may be an effective solution. However, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen. They can help determine the best form of B12 for your needs and recommend a safe and effective dosage.
References
- Journal of Andrology. (2010). Vitamin B12 supplementation improves sperm count and motility in infertile men.
- Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. (2010). Vitamin B12 supplementation improves sperm count, motility, and morphology in men with low levels of this nutrient.