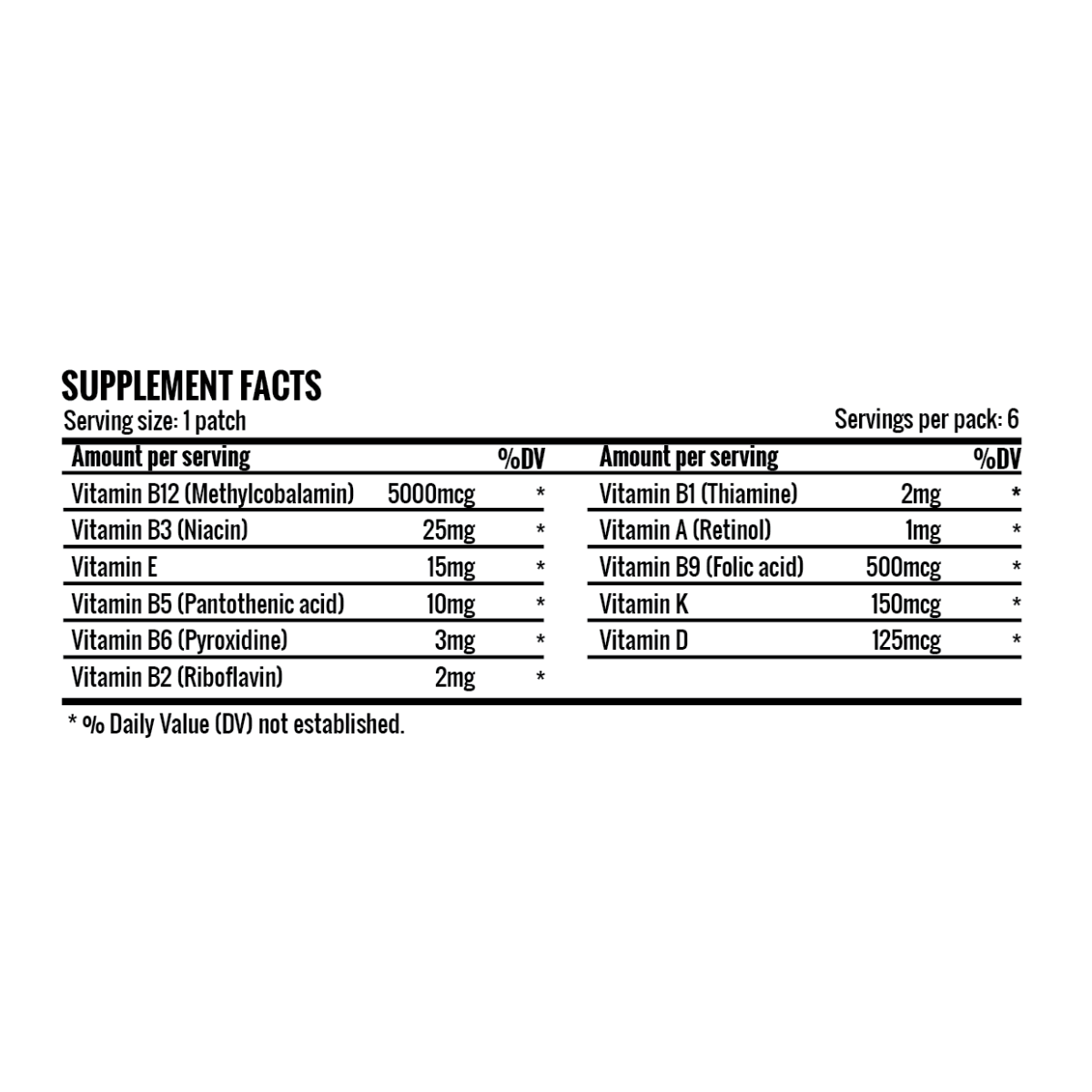
There are eight B-Vitamins that are commonly referred to as vitamin B Complex. This comprises of vitamins B1, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and B12. All of these B-Vitamins play a different role in maintaining and supporting various functions and activities inside our body. These essential nutrients help the body process food into usable energy, keeping us energized throughout the day. These vitamins work in tandem with each other but each of them has its own benefit that vary from each other, ranging from brain health, skin, energy accumulation, and digestion, among other things.
Here are the different types of B-Vitamins and their respective functions and benefits:
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Also known as Vitamin B1, Thiamine helps the body make healthy new cells and produce cellular energy from the foods that you eat. It’s often called an anti-stress vitamin because of its ability to protect the immune system. Thiamine is also known to support the nervous system. Thiamine is necessary to help break down those simple carbohydrates. It is found in a wide variety of foods, such as lentils, whole grains and pork. Thiamine can also be found in red meats, yeast, nuts, kale, blackstrap molasses, wheat germ, sunflower seeds, peas, milk, cauliflower, spinach, whole grains, and legumes.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Riboflavin often works as an antioxidant to help fight free radicals from damaging the cells and may help prevent early aging and the development of heart disease. Vitamin B2 also supports cellular energy production and is important for red blood cell production, which is necessary for transporting oxygen throughout the body. Vitamin B2 is known to help stave off migraines. Food sources that contain Riboflavin include cereals, milk, eggs, salmon, beef, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, wild rice, almonds, and spinach.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Niacin helps boost good cholesterol or HDL cholesterol. The higher the HDL level of a person is, the lower the LDL or bad cholesterol level. Alcoholism may lower levels of this B-vitamin among some individuals. Niacin also helps support cardiovascular health and may be found in food sources such as beef, fish, poultry, whole wheat bread, peanuts, yeast, milk, eggs, bean, and lentils, as well as green vegetables.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Pantothenic comes from the word pantothen which means from everywhere since this nutrient can be found in almost all food groups, albeit in small amounts. It helps break down fats and carbs and processes it to usable energy. Vitamin B5 is so responsible for producing cortisol and testosterone, hormones that are needed for stress-response and sexual behavior. Vitamin B5 s also said to promote healthy skin and helps reduce signs of aging. It is available in organ meats such as liver and kidney, as well as in egg yolk, avocados, cashew nuts, milk, peanuts, lentils, soybeans, broccoli, yogurt, legumes, and brown rice.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Vitamin B6 is involved in over 100 cellular reactions and helps regulate levels of the amino acid homocysteine (associated with heart disease). Pyridoxine is vital for mood and sleep patterns because it helps the body produce serotonin, melatonin, and norepinephrine, a stress hormone. Pyroxidine is also vital in the metabolism of amino acids and glycogen as well as for the nervous system and red blood cell formation. You can get Vitamin B6 from chicken, tuna, eggs, banana, fish, fortified cereal grains, carrots, brown rice, cheese, salmon, lentils, and cooked spinach.
Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
Vitamin B7 is associated with having healthy hair, skin, and nails. It also It may help people with diabetes control high blood glucose levels. It is vital or pregnant women to take this vitamin for the normal growth of the baby. Biotin also supports carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism into energy. Food sources of biotin include barley, liver, yeast, brewer’s yeast, pork, chicken, fish, potatoes, cauliflower, cheese, soybeans, egg yolks, and nuts.
Vitamin B9 (Folate)
Folic acid, folate, or vitamin B9 is an essential nutrient that is vital for the roles it plays in the body. It is known for its role in fetal health and development for the baby. Pregnant women are encouraged to take folate. It also helps prevent memory loss and depression. Folate may also help reduce a pregnant woman’s risk of having a child with a neural tube defect. Food sources of folate may include fortified food sources such as such as bread and cereals are good dietary sources of folic acid. Natural sources of folate include dark green leafy vegetables such as asparagus and spinach as well as brewer’s yeast, liver, fortified orange juice, beets, salmon, root vegetables, milk, bulgur wheat, dates, and avocados.
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
We have stressed on the numerous benefits you can get out of Vitamin B12. It doesn’t stop there. Vitamin B12 is a team player, which means it works with the other B-Vitamins to help improve the body. It helps vitamin B9 produce red blood cells and aid iron to produce red blood cells. It also plays a critical role in the pathways of the body that produce cellular energy, DNA synthesis, and helps in the red blood cell formation, and helps maintain nervous system function. Vitamin B12 is found in meats such as beef, chicken, fish, and milk.
Having Vitamin B12 is beneficial for the body but having all the B-vitamins can help amplify the positive effects of Vitamin B12. It is about having a balance of all the nutrients in the body and vitamin B12 is one of the many nutrients and B-vitamins that you should take in order for the body to function as healthy as it should.
References:
Naturemade.com. (2016). A Guide to the B Vitamins. [online] Available at: http://www.naturemade.com/resource-center/articles-and-videos/energy/get-buzzing-with-bs#C2r1H1Bk4YUM52Yp.99 [Accessed 9 Dec. 2016].
McDermott, N. and McDermott, N. (2016). The Benefits of Vitamin B Complex – Life by Daily Burn. [online] Life by Daily Burn. Available at: http://dailyburn.com/life/health/benefits-vitamin-b-complex/ [Accessed 9 Dec. 2016].
Naturemade.com. (2016). A Guide to the B Vitamins. [online] Available at: http://www.naturemade.com/resource-center/articles-and-videos/energy/get-buzzing-with-bs [Accessed 9 Dec. 2016].
Cold, F., Health, E., Disease, H., Management, P., Conditions, S., Problems, S., Disorders, S., Checker, S., Interviews, E., Boards, M., Guide, I., Doctor, F., Medications, M., Identifier, P., Interactions, C., Drugs, C., Pregnant, T., Management, D., Obesity, W., Recipes, F., Exercise, F., Beauty, H., Balance, H., Relationships, S., Care, O., Health, W., Health, M., Well, A., Teens, H., Kids, F., Pregnant, G., Trimester, F., Trimester, S., Trimester, T., Baby, N., Health, C., Vaccines, C., Kids, R., Cats, H., Dogs, H., Adults, C., Ears, T., Stuttering, S., Regular Drinkers, I., Town, V., Boards, M., Blogs, E., Center, N. and Recipes, F. (2016). Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment. [online] WebMD. Available at: http://www.webmd.com/food-recipes/guide/vitamin-b12-deficiency-symptoms-causes#1 [Accessed 9 Dec. 2016].