When it comes to skincare, the appearance of acne and eczema is one of the most common concerns. These skin conditions can cause discomfort, pain, and embarrassment, making it difficult for those who suffer from them to go about their daily lives confidently. Acne is a skin condition caused by clogged hair follicles with oil and dead skin cells, resulting in pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. Eczema, on the other hand, is a skin condition that causes itchy, red, and dry patches of skin. Acne and eczema can both be caused by a variety of factors such as genetics, hormonal imbalances, stress, and diet.
While there are several treatments for these conditions, including topical creams, oral medications, and lifestyle changes, many people are turning to Vitamin B12 as a natural and effective way to relieve symptoms. Vitamin B12 is a necessary nutrient that aids in the growth and repair of skin cells, making it an excellent supplement for those suffering from acne or eczema. Vitamin B12 has numerous other benefits for overall health and wellbeing, including supporting the nervous system, increasing energy levels, and aiding in the formation of red blood cells.
By increasing your intake of Vitamin B12, whether through foods like meat, fish, and dairy or supplements, you can help alleviate acne and eczema symptoms and achieve healthier, more vibrant skin. However, before beginning any new supplements or making significant changes to your diet, you should consult with a healthcare professional. You can regain control of your skin's health and enjoy a brighter, clearer complexion with the right approach.
History
Vitamin B12 was discovered in the early twentieth century and was initially referred to as the "extrinsic factor" due to its critical role in the prevention of pernicious anemia. Researchers have discovered that Vitamin B12 is essential for a variety of bodily functions, including the production of healthy skin cells.
How it works
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that is required for many bodily functions, including skin cell growth and repair. It functions by playing an important role in DNA synthesis, which is required for cell division and growth. Without enough Vitamin B12, the body is unable to produce healthy skin cells, leading to a variety of skin problems such as acne and eczema.
Vitamin B12, in addition to promoting skin cell growth and repair, aids in the regulation of sebum production. Sebum is an oily substance produced by the skin's sebaceous glands. Excessive sebum production can clog pores and cause acne. Vitamin B12 regulates sebum production, lowering the chances of clogged pores and acne breakouts.
Vitamin B12 also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help with eczema symptoms. Eczema is a skin condition characterized by inflammation and dryness. Vitamin B12, by reducing inflammation, can help relieve itching, redness, and discomfort associated with eczema.
It is critical to note that, while Vitamin B12 can be beneficial to skin health, it is not a panacea for all skin problems. Maintaining a balanced and healthy diet, practicing good skincare habits, and seeking medical advice when necessary are all essential.
In general, Vitamin B12 is an important nutrient for skin health. Vitamin B12 can help alleviate acne and eczema symptoms and promote healthy, vibrant skin by supporting skin cell growth and repair, regulating sebum production, and reducing inflammation.
Studies and Results
Numerous studies have been conducted to investigate the relationship between Vitamin B12 and skin health, specifically the relief of acne and eczema symptoms. Researchers examined the Vitamin B12 levels of 100 participants with and without acne in one study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology. The participants with acne had significantly lower levels of Vitamin B12 than those without acne, according to the findings. This suggests that maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin B12 may aid in the prevention or treatment of acne.
Researchers looked at the effectiveness of Vitamin B12 supplements in treating eczema symptoms in another study published in the British Journal of Dermatology. The study included 49 eczema patients who were randomly assigned to either a Vitamin B12 supplement or a placebo for eight weeks. When compared to those who received the placebo, those who received the Vitamin B12 supplement experienced a significant reduction in eczema symptoms such as itching, redness, and scaling.
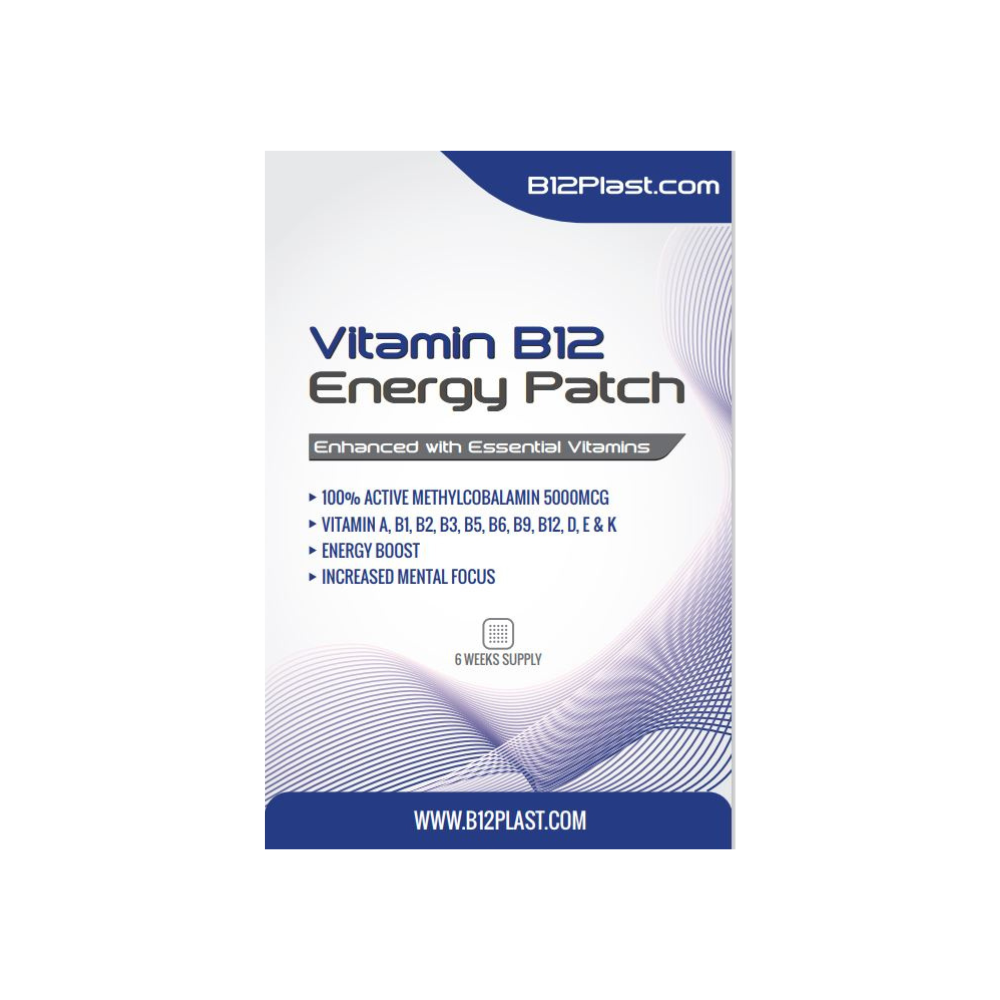
The recommended Vitamin B12 dosage varies according to age, gender, and individual needs. The participants in the eczema study mentioned above received a daily dose of 1,500 mcg of Vitamin B12. However, high doses of Vitamin B12 can be harmful, so consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any supplements or making significant changes to your diet.
Overall, the research suggests that Vitamin B12 can be an effective supplement for treating acne and eczema symptoms. Individuals may be able to reduce their symptoms and promote healthy skin by maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin B12 through diet or supplements. More research is needed, however, to fully understand the relationship between Vitamin B12 and skin health, as well as the optimal dosage for different individuals.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin B12 varies depending on age and gender. However, most adults require around 2.4 mcg per day. While it's possible to get Vitamin B12 from foods such as meat, fish, and dairy, some people may require supplements to ensure they're getting enough of this essential nutrient.
Conclusion
If you suffer from skin conditions such as acne or eczema, increasing your intake of Vitamin B12 may be beneficial. Vitamin B12 can help improve the health and appearance of your skin by promoting skin cell growth and repair, regulating sebum production, and reducing inflammation.
References
Reynolds, E. Vitamin B12, folic acid, and the skin. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28(1):27-33.
Capodanno, D., & Guarneri, F. (2018). Vitamin B12 in dermatology. Indian dermatology online journal, 9(6), 491–496.
Ebede, T. L., Arch, E. L., & Berson, D. (2009). Hormonal treatment of acne vulgaris: an update. American journal of clinical dermatology, 10(4), 281– 292.